The bond between a mother and her infant is one of the most extraordinary and profound connections in the human experience. It transcends the boundaries of biology and is woven from the threads of love, care, and instinct. This special relationship plays a crucial role in shaping the emotional and psychological well-being of both the mother and the child.
-
Biological Foundation: At the core of this connection lies a biological foundation that begins during pregnancy. The mother’s body nurtures and sustains the developing infant, creating an intimate physical bond before birth. This prenatal period is marked by a unique exchange of hormones and nutrients that lay the groundwork for the emotional ties that will follow.

-
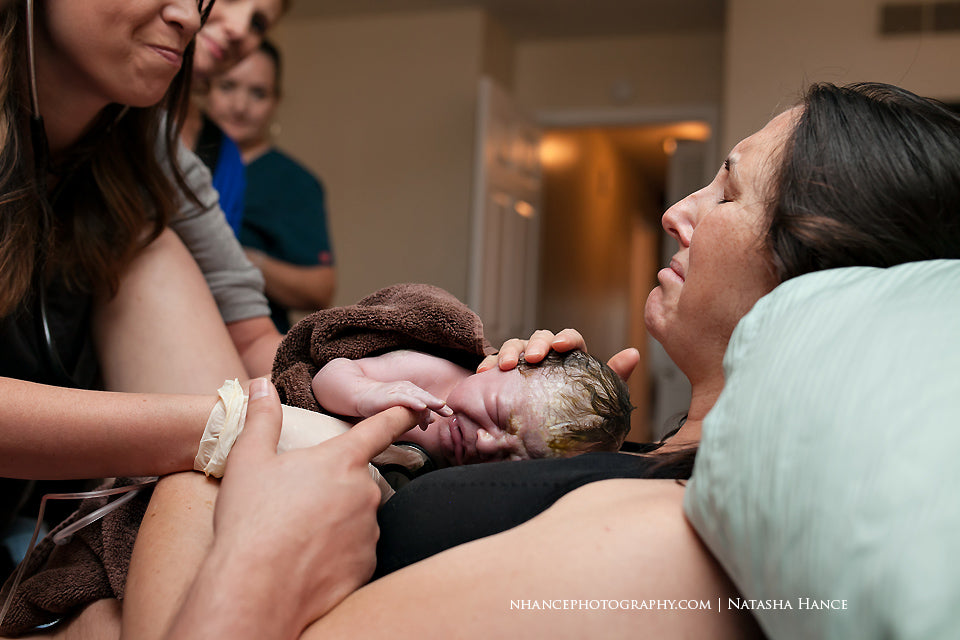
Birth and the First Moments: The moment of birth is a monumental transition for both mother and infant. The first contact between the two, often through skin-to-skin contact, triggers a cascade of neurochemical reactions that promote bonding. The touch, smell, and sound of the mother become integral elements in the infant’s early sensory experiences, fostering a sense of security and trust.
-
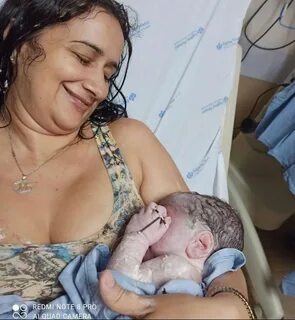
Mutual Attachment: The process of attachment is reciprocal. The infant instinctively seeks closeness and comfort from the mother, while the mother is biologically primed to respond to her infant’s needs. This mutual attachment is not only a source of physical nourishment but also lays the foundation for emotional and social development.

-
Communication Beyond Words: In the early stages of life, infants communicate primarily through non-verbal cues. The mother becomes attuned to her baby’s subtle signals, responding to cries, facial expressions, and body language. This non-verbal communication is a powerful means through which the emotional bond is strengthened.

-
Emotional Development: The emotional security provided by a nurturing mother-infant relationship has long-lasting effects on the child’s emotional development. A secure attachment fosters a sense of trust and confidence, which becomes the basis for future relationships and emotional resilience.

-
Maternal Instinct and Protective Love: Maternal instinct, often described as an innate understanding of a mother for her child’s needs, plays a crucial role in the relationship. The intense, protective love a mother feels creates a secure environment for the infant to explore and learn about the world.

-
Long-Term Impact: The impact of a strong mother-infant bond extends well beyond infancy. Research suggests that children who experience secure attachments tend to develop better cognitive abilities, emotional regulation, and social skills. The mother’s influence continues to shape the child’s life, providing a stable foundation for their journey into adolescence and adulthood.
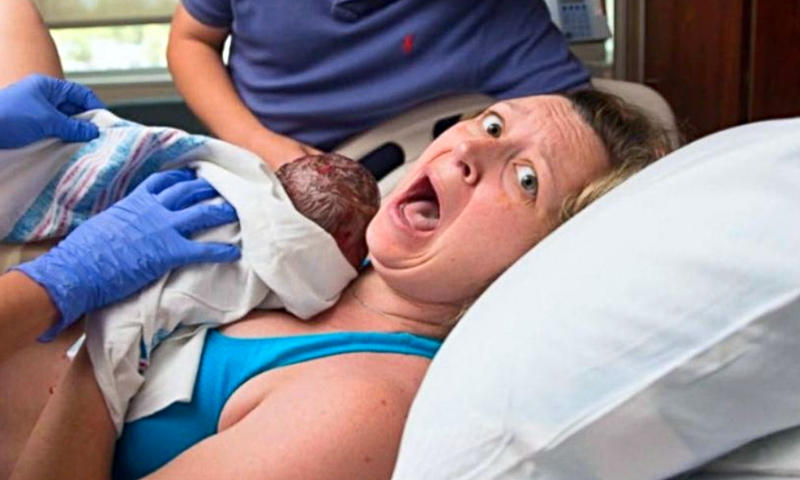
In conclusion, the relationship between a mother and her infant is a profound and multifaceted connection that begins before birth and continues to evolve throughout life. It is a testament to the intricate interplay of biology, psychology, and love, creating a bond that is unparalleled in its significance and depth. The nurturing care and emotional support provided by a mother lay the groundwork for a child’s healthy development, illustrating the enduring impact of this extraordinary relationship.
